What is Profit Margin?
A company’s profit margin is a measure of its earnings relative to its revenue. The most common measure, the margin expresses earnings as a percent of sales. It is an indicator of how well the company is performing financially.
There are 3 Types of Profit Margin – GROSS PROFIT MARGIN, NET PROFIT MARGIN & OPERATING PROFIT MARGIN that help in evaluating a company’s financial health.
Gross Profit Margin
Gross profit margin, also referred to as gross margin, is a measure of a company’s profitability. Gross profit margin indicates the amount of revenue remaining in a given accounting period after a company pays for labor and materials, otherwise known as cost of goods sold (COGS).
Any company’s gross profit margin is the most basic measure of a company’s profitability. It shows how much money is left in the coffers after accounting for the cost of producing goods and services and paying workers. Entrepreneurs and investors look forward to see a good gross profit margin. When Gross Margin is shrinking, it is either a sign that the business is investing in its operations or it has a problem.

Gross Margin Formula
Gross profit margin is computed by dividing the difference between total revenue and the cost of goods or services sold by total revenue, and is generally represented as a percentage.
Net Profit Margin
Net Profit Margin or Net Profit Margin Ratio is a ratio used to calculate the percentage of profit a company earns from its total revenue. It measures the amount of net profit a company obtains per rupee of revenue gained. The net profit margin is equal to net profit (also known as net income) divided by total revenue. It is expressed as a percentage.
The typical profit margin ratio of a company can be different depending on which industry the company is in.
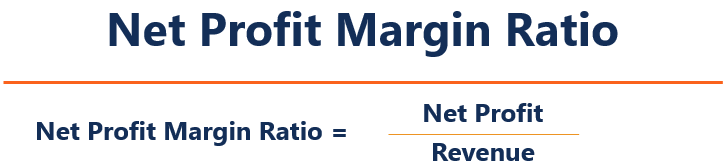
Net Profit Margin Formula
Net Profit margin = Net Profit ⁄ Total revenue x 100
The net profit margin ratio is the percentage of a business’s revenue left after deducting all expenses from total sales, divided by net revenue.
Net profit is calculated by deducting all company expenses from its total revenue. The result of the profit margin calculation is a percentage – for example, a 10% profit margin means for each ₹1 of revenue the company earns ₹0.10 in net profit. Revenue represents the total sales of the company in a period.
Operating Profit Margin
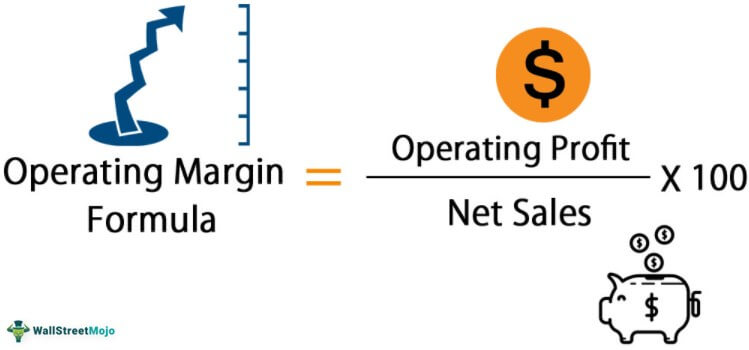
Operating Profit Margin includes Costs of Goods Sold (COGS), costs associated with selling and administration of the product or service, and overhead. The COGS formula remains same across most industries, but what is included to calculate COGS varies for each industry. The Operating Profit Margin creates a relationship between the operating income of a company (i.e. earnings before interest and taxes, or “EBIT”) and revenue to estimate the profits made prior to paying off non-operating expenses.
Operating Profit Margin varies in magnitude across industries and is often used as a benchmarking matric between one company against similar companies within the same industry. It tends to reveal the top performers within an industry. It also provides an insight into the need for further research regarding why a particular company is outperforming or falling behind its peers.
Operating Profit Margin Formula
The operating profit margin calculation is the percentage of operating profit derived from total revenue.
Profit margins, in a way, help determine the supply for a market economy. If a product or service doesn’t create a profit, companies will not supply it. All the 3 type of Profit Margins help in securing funding from prospective investors as they look at the health of the companies through these paramaters, amongst other parameters. higher the margins, beter is the overall health of the company and ensures it’s existance for a longer period of time.

